The psychology of emotional eating
The psychology of emotional eating: Understanding triggers & coping strategies. Discover the psychology of emotional eating & learn how to identify triggers & effective coping strategies to manage your relationship with food, and we have to know how to glow natural wellness.
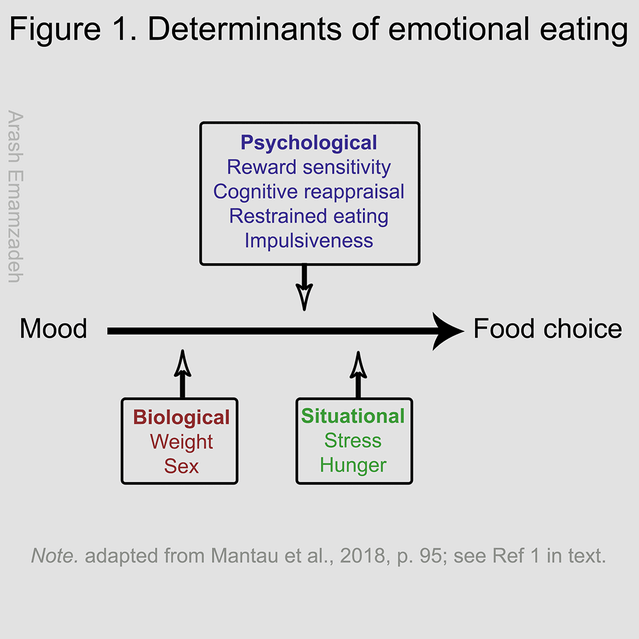
What is Emotional Eating?
Emotional eating refers to the practice of consuming food in response to feelings rather than hunger. This often occurs when individuals seek comfort or relief from discomforting emotions. Personal experiences with emotional eating can vary widely; for instance, I have found myself reaching for snacks during stressful periods, treating food as a source of solace. Essentially, it’s a coping mechanism for many, providing a temporary escape or distraction from negative emotions. Be that as it may, it often leads to unhealthy eating patterns & emotional distress in the long run. Recognizing & defining emotional eating is the first essential step towards healthier habits & emotional well-being, and we have to how to glow natural wellness
Common Triggers of Emotional Eating
Emotional eating is often precipitated by various triggers that can vary from person to person. Understanding these triggers is crucial for managing emotional eating behaviors effectively. Common triggers include stress, boredom, loneliness, & sadness. Stress can lead individuals to seek solace in food to cope with feelings of overwhelm, while boredom might push someone to snack mindlessly. Loneliness & sadness often create a yearning for comfort, & food can temporarily fill that void.
| Trigger Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Stress | Heightened anxiety or tension leading to food cravings. |
| Boredom | Eating out of habit rather than genuine hunger. |
| Loneliness | Using food as a companion when feeling isolated. |
| Sadness | Turning to food for comfort during low moods. |
Recognizing these triggers is essential. It allows individuals to identify their emotional eating patterns & find healthier coping strategies. Keeping a food journal may help in recognizing these triggers, allowing for greater self-awareness & control.
The Role of Habits in Emotional Eating
Habits play a significant part in emotional eating, often becoming automatic responses to certain feelings or circumstances. When someone consistently turns to food in times of emotional unrest, this behavior becomes a reinforcement loop. Each time food provides momentary comfort, it strengthens the association between emotional distress & eating. Over time, these habits can become ingrained, leading to a cycle that is tough to break. For example, someone might habitually order takeout when feeling overwhelmed instead of finding productive ways to address their feelings.
- Identify your eating habits linked to emotions.
- Consider seeking healthier alternatives or coping mechanisms.
- Set specific times for meals instead of eating mindlessly.
Changing these ingrained habits can be challenging, but it is possible with dedication & awareness. Gradually introducing healthier routines & mindfulness into the eating process can help in diminishing the power of emotional triggers.
Healthy Alternatives to Emotional Eating
Finding alternatives to emotional eating is vital for individuals seeking to break the cycle. Instead of reaching for food when feeling down or stressed, explore healthier responses such as physical activities, social interaction, or creative outlets. Engaging in exercise, for instance, has both physical & psychological benefits; it releases endorphins, which can enhance mood & reduce stress levels.
| Alternative Activity | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Exercise | Boosts mood & reduces stress. |
| Meditation | Promotes mindfulness & emotional regulation. |
| Journaling | Helps process feelings effectively. |
| Spending Time with Friends | Alleviates feelings of loneliness. |
Incorporating these alternatives into daily life encourages healthier emotional coping strategies. Creating a list of activities that can replace emotional eating is an effective way to visualize options in challenging moments.
Mindfulness & Emotional Eating
Practicing mindfulness can significantly mitigate emotional eating by fostering a greater awareness of thoughts & feelings. Mindfulness involves being present in the moment & observing emotions without judgment. This practice allows individuals to recognize emotional triggers & differentiate between actual hunger & emotional distress. Techniques such as mindful meditation, deep breathing, or yoga can ground individuals, steering them away from unhealthy eating habits.
- Take a moment to breathe deeply when feeling the urge to eat emotionally.
- Reflect on your emotions before engaging with food.
- Practice mindfulness in every meal to appreciate flavors & textures.
Engaging fully during meals enhances the eating experience & helps control overeating. By being mindful, individuals can break the cycle of emotional eating while also cultivating a healthier relationship with food.
Seeking Professional Help
In some cases, emotional eating can be a symptom of deeper emotional or psychological issues that may require professional assistance. Therapists & counselors can provide valuable insights & coping strategies tailored to individual needs. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), for example, has proven effective in addressing emotional eating by altering thought patterns associated with food & emotional distress. They can help individuals develop healthier coping mechanisms & improve emotional regulation.
| Professional Help Options | Description |
|---|---|
| Therapy | Guided sessions aimed at understanding emotional triggers. |
| Nutritional Counseling | Learning about healthy eating habits without emotional ties. |
| Support Groups | Sharing experiences with others facing similar issues. |
Engaging with trained professionals can provide a roadmap to understanding & managing emotional eating more effectively. Whether it’s through therapy or community support, seeking help is a strong step towards emotional well-being.
Long-Term Strategies for Change
Creating long-term strategies is essential for those who wish to combat emotional eating successfully. It involves setting realistic goals & maintaining a consistent practice around awareness of emotional triggers & healthy responses. One effective strategy is to create a balanced life that promotes emotional well-being. This includes factors like regular exercise, adequate sleep, & social connectivity. Keeping a food diary can also create insight into eating patterns, clarifying when & why emotional eating occurs.
- Establish a routine with scheduled meals & snacks.
- Create an emotional trigger chart to identify specific scenarios.
- Set achievable goals for healthier eating habits.
On top of that, patience & self-compassion are critical components in this journey. Acknowledging setbacks without judgment encourages resilience & long-term change.
Coping Techniques to Manage Emotional Eating
Implementing coping techniques can be beneficial in addressing emotional eating triggers. Journaling can be an excellent outlet for emotions, helping individuals articulate feelings before reacting with food. Another effective strategy is practicing gratitude; reflecting on what one is thankful for can shift focus away from negative emotions. Avoiding situations that ignite emotional eating urges is also a practical approach; for example, individuals might choose to avoid certain environments or situations that trigger the desire to eat out of dissatisfaction.
| Coping Technique | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Journaling | Provides a safe space to express emotions. |
| Practicing Gratitude | Shifts focus from negative emotions to positive aspects. |
| Exercise | Releases endorphins, improving mood. |
Creating a personalized toolbox of coping techniques can empower those dealing with emotional eating by providing diverse methods to cope with feelings without resorting to food.
The Importance of Community Support
Building a support network can play a pivotal role in overcoming emotional eating. Friends, family, or support groups provide the encouragement & accountability necessary for success. Sharing experiences with others who face similar challenges can foster connection & reduce feelings of isolation. Whether through informal social gatherings or structured support groups, connecting with others promotes kindness & understanding.
- Identify friends or family members who understand your challenges.
- Consider attending local support groups or online communities.
- Engage in social activities that promote health & well-being.
Eliminating the stigma surrounding emotional eating & reaching out for support will not only enhance recovery efforts but also develop resilience in the face of inevitable challenges.
“The psychology of emotional eating can act like a double-edged sword, reflecting not just our relationship with food, but more profoundly our emotional well-being.” – Art Mraz II
Recognizing the Impact of Emotional Eating on Health
The implications of emotional eating extend beyond the behavioral, significantly influencing physical health. Over time, emotional eating can lead to weight gain, obesity, & associated health complications, such as diabetes & heart disease. On top of that, the cycle of using food as an emotional salve can perpetuate poor nutritional choices, compounding health issues. Recognizing these impacts is essential for individuals seeking to understand the psychology of emotional eating fully.
| Health Impact | Description |
|---|---|
| Weight Gain | Increased caloric intake from emotional eating. |
| Heart Disease | Unhealthy eating habits lead to increased cholesterol & heart strain. |
| Mental Health Issues | Struggles with emotions can lead to anxiety & depression. |
| Diabetes | Higher consumption of sugars & unhealthy foods is impacting blood sugar. |
Awareness of these health impacts on one’s life can be a motivating factor in pursuing healthier habits, marking the start of a journey toward emotional & physical wellness.
Setting Realistic Goals for Managing Emotional Eating
Setting realistic goals offers a structured approach to dealing with emotional eating. Goals can provide direction & a sense of accomplishment as they are achieved. Instead of aiming for drastic lifestyle changes, focus on small, attainable targets, such as reducing the frequency of emotional eating incidents or introducing one healthy meal per day. Reflection on goals regularly can ensure they remain relevant & motivating.
- Start with one small change, like substituting a snack with fruit.
- Celebrate achievements to reinforce positive behavior.
- Set aside regular time for self-reflection regarding progress.
Revising goals based on progress is crucial; flexibility allows for adaptation, enabling ongoing growth away from emotional eating.

What is emotional eating?
Emotional eating is the practice of consuming food in response to feelings rather than hunger. Individuals engage in this behavior as a way to cope with emotions such as stress, boredom, anxiety, or sadness, often leading to overeating or choosing unhealthy foods.
What are the triggers for emotional eating?
Triggers for emotional eating can vary widely among individuals but commonly include stress, negative emotions, boredom, social situations, or specific environmental cues like the sight or smell of food. Recognizing these triggers can help individuals manage their eating habits more effectively.
How does emotional eating affect mental health?
Emotional eating can create a cycle where negative feelings are temporarily alleviated by food, but lead to guilt, shame, & further emotional distress afterward. This cycle can exacerbate issues like anxiety, depression, & low self-esteem, ultimately affecting overall mental health.
What are some coping strategies for emotional eating?
Coping strategies for emotional eating include practicing mindfulness, identifying emotional triggers, developing healthier alternatives to deal with emotions, keeping a food journal, & seeking support from friends, family, or professionals to better understand & manage emotions related to food.
Can emotional eating be treated?
Yes, emotional eating can be treated through various therapeutic approaches including cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), mindfulness practices, nutritional counseling, & support groups. Treatment focuses on addressing the underlying emotional issues & developing healthier coping mechanisms.
How can I differentiate between emotional hunger & physical hunger?
Emotional hunger often comes on suddenly & feels urgent, while physical hunger develops gradually & can be satisfied with a variety of foods. And another thing, emotional hunger typically craves specific comfort foods & can lead to eating without awareness, whereas physical hunger involves a stronger focus on nutrition.
Is emotional eating common?
Yes, emotional eating is a common behavior. Many individuals cope with their feelings through food at some point in their lives. Understanding that it is a widespread issue can help reduce feelings of isolation or shame associated with emotional eating.
Are there specific foods that contribute to emotional eating?
Comfort foods, often high in sugar, fat, or carbohydrates, tend to be the go-to choices for emotional eaters. These foods can momentarily enhance mood, but over time may lead to unhealthy eating patterns & contribute to weight gain or health issues.
How can one start addressing emotional eating?
Addressing emotional eating begins with self-awareness & recognizing emotional triggers. Developing healthier coping mechanisms, such as physical activity, journaling, or engaging in hobbies, can help replace the desire to eat in response to emotions.
What role does stress play in here?
Stress is a significant factor in emotional eating, as it can lead to feelings of overwhelm or anxiety. Many individuals respond to stress by seeking comfort in food, making it important to find alternative ways to manage stress, such as exercise, meditation, or talking to a friend.
Can mindfulness help with this?
Yes, mindfulness can be an effective tool for managing emotional eating. By practicing mindfulness, individuals can develop a greater awareness of their eating habits, recognize emotional triggers, & create a healthier relationship with food by focusing on the experience of eating, rather than using it as an escape.

Conclusion
In understanding the psychology of emotional eating, we see how our feelings often dictate our food choices. Recognizing triggers like stress, boredom, or sadness is the first step to taking control. By applying simple coping strategies, such as finding healthier alternatives or engaging in activities we enjoy, we can manage those emotional cravings. Remember, it’s okay to seek support when needed. Awareness is key, & by learning more about the psychology of emotional eating, we empower ourselves to make better choices. Let’s embrace healthier habits & nurture our emotional well-being while enjoying food mindfully.



